Understanding Business and Revenue Models: Creating Value and Driving Profitability:
The business model describes the functioning and important factors of a company. The business model helps you to identify, analyse and improve the key factors of your company. It answers the question of how your company generates value, what you deliver to customers and how you set yourself apart from the competition.
Revenue models show you how you can generate profits. Revenue models come in different forms, and the internet in particular has created many new revenue models. We provide you with an overview of the most common and important revenue models and show you which model is right for your company.
Video 1: Business Model Navigator
Video 2: Innovative revenue models
The revenue model describes from which sources and in which way income is generated. There are different ways in which a company can earn money. Here we show you the most important content and key questions that you can use to develop your revenue model.
Additional content: Business Model Canvas
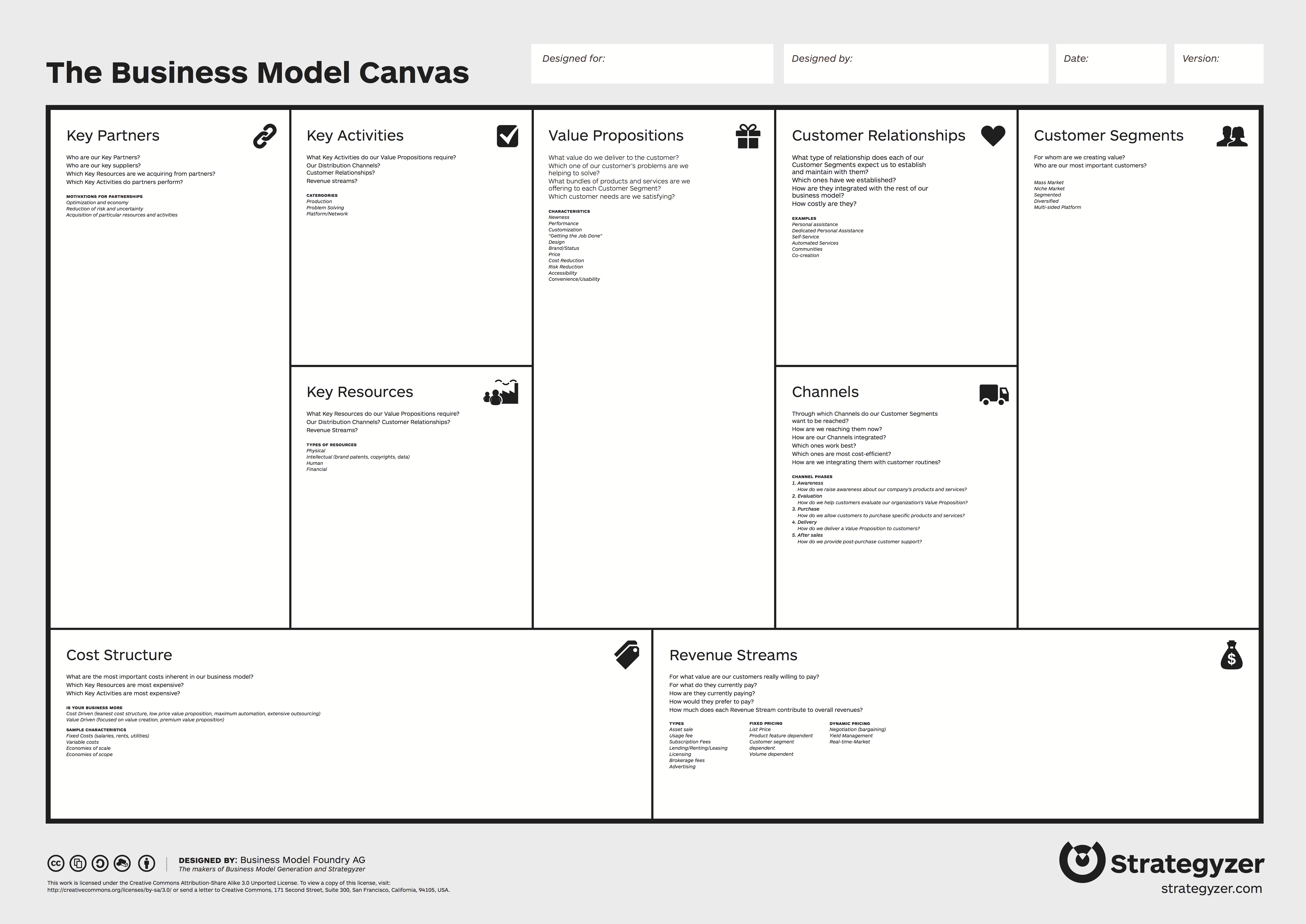
The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a strategic framework that helps businesses design, visualize, and refine their business models. Developed by Alexander Osterwalder, it is widely used by startups, entrepreneurs, and established companies to understand how they create, deliver, and capture value.
Unlike traditional business plans that can be long and rigid, the BMC provides a clear, one-page overview of the key components of a business. It allows for agile adjustments, ensuring that business owners can quickly test ideas, identify gaps, and make improvements without spending too much time writing long documents.
The BMC is divided into nine key building blocks, which are categorized into four main areas:
📌Offering (What value is being provided to customers?)
📌Customers (Who are the customers and how do they interact with the business?)
📌Infrastructure (What is needed to run the business?)
📌Finances (How does the business generate and manage money?)
1. Value Proposition – What makes your business unique?
The value proposition is the core of the Business Model Canvas. It defines why customers should choose your product or service over competitors.
- Innovation: Offering something entirely new.
- Performance: Improving existing products/services.
- Customization: Tailoring solutions to specific customer needs.
- Convenience: Making life easier for the customer.
- Price: Offering a better deal than competitors.
2. Customer Segments – Who are your customers?
A customer segment is a specific group of people or businesses that a company targets with its products or services.
- Mass Market: Broad appeal (e.g., Coca-Cola).
- Niche Market: Specialized audience (e.g., luxury watches).
- Segmented Market: Different versions for different audiences.
- Multi-sided Market: Serving two or more groups (e.g., Uber connects drivers and passengers).
3. Customer Relationships – How do you interact with your customers?
- Personal Assistance: Direct customer support.
- Self-Service: Customers help themselves (e.g., FAQs).
- Automated Services: AI chatbots and recommendation engines.
- Communities: Engaging customers in a shared space (e.g., Apple forums).
4. Channels – How do you deliver value to customers?
- Own physical stores or online platforms?
- Partner stores or marketplaces?
- Direct sales vs. indirect sales through intermediaries?
5. Key Partners – Who supports your business?
Key partners are external companies, suppliers, or stakeholders that support the business by providing essential resources, services, or capabilities.
- Strategic alliances: Non-competitors working together for mutual benefit.
- Joint ventures: Businesses creating a new entity together.
- Supplier relationships: To secure raw materials or essential services.
- Outsourcing: Delegating certain business functions to external providers.
6. Key Activities – What do you need to do to succeed?
Key activities refer to the most important tasks and processes a business must perform to operate successfully and deliver its value proposition.
- Production: Manufacturing or creating a product.
- Problem-solving: Consulting, customer support, or service-based businesses.
- Platform management: Running an app, website, or software.
7. Key Resources – What assets are essential for your business?
Key resources are the assets required to operate and deliver value to customers. They can be tangible (physical) or intangible (intellectual).
- Physical: Offices, machinery, warehouses.
- Intellectual: Patents, trademarks, brand reputation.
- Human: Skilled employees, expert knowledge.
- Financial: Investment capital, credit lines.
8. Revenue Streams – How does the business make money?
- Product sales (one-time purchases).
- Subscription models (Netflix, Spotify).
- Freemium models (basic service for free, premium features paid).
- Licensing and franchising.
9. Cost Structure – What are the main costs?
- Fixed costs: Rent, salaries, long-term contracts.
- Variable costs: Manufacturing, raw materials, marketing.
- Economies of scale: Reducing costs as production increases.
Final Thoughts: Why Use the Business Model Canvas?
The Business Model Canvas is a powerful tool for startups and established businesses alike. Its clear and structured format enables:
- ✅ Quick business planning.
- ✅ Efficient strategy testing.
- ✅ Easy collaboration among teams.
- ✅ A customer-centric approach.
Examples of revenue models
💰 1. Direct Sale (One-Time Payment)
In direct sales, a company sells a product or service to a customer for a one-time payment. This model is classic, easy to understand, and widely used.
Example: AVM (Fritz!Box) sells routers and devices directly to end customers.
✅ Advantages: Immediate revenue, Easy to calculate
❌ Disadvantages: No recurring revenue, Continuous need for customer acquisition
🔁 2. Subscription Model
The customer pays regularly (monthly or yearly) for access to a product or service.
Example: Deutsche Telekom – Mobile and internet contracts with monthly fees. Or SaaS models for using specific software.
✅ Advantages: Predictable, recurring revenue, Long-term customer retention
❌ Disadvantages: Higher service workload, Risk of cancellations if unsatisfied
🎁 3. Freemium Model
Description: Basic service is free, additional features are paid.
Example: NetSpot or WiFi Analyzer Apps offer free basic features and paid pro versions.
✅ Advantages: Low entry barrier, Fast growth possible
❌ Disadvantages: Low conversion rate from free to paid users, High infrastructure costs possible
🧠 4. Licensing
Use of a product (e.g., technology or software) is permitted to other companies in return for license fees.
Example: A startup develops an innovative 6G antenna design and licenses it to large manufacturers.
✅ Advantages: High margin, Low production costs, Potentially scalable
❌ Disadvantages: Dependency on licensees, Protection via IP rights required – often expensive, especially internationally
👥 5. Brokerage Model
Description: Revenue is generated by brokering transactions between third parties.
Example: Check24 for telecom tariffs – earning commissions for mediation.
✅ Advantages: No own product needed, Low risk
❌ Disadvantages: Dependency on partners, Margins can be low
🏷 6. Advertising Model
Description: Products or content are free – revenue comes from advertising.
Example: YouTube channels about tech products or Telekom blogs with sponsored content.
✅ Advantages: Free offering for users, Reach becomes a currency
❌ Disadvantages: Dependency on advertisers, Data privacy concerns
🛠 7. Pay-per-Use
Description: Billing only occurs based on actual usage.
Example: Cloud services for network analysis that charge based on data volume.
✅ Advantages: Low entry costs for customers, Fair and flexible
❌ Disadvantages: Fluctuating revenues, Difficult to plan
📦 8. Bundling
Description: Combining multiple services into one overall price.
Example: Telekom MagentaEINS – landline, mobile, and streaming in one package.
✅ Advantages: Higher perceived value, Customer loyalty through convenience
❌ Disadvantages: Complex pricing, Risk of cannibalizing individual products
🏗 9. Platform Model
Description: The platform operator connects providers and consumers – revenue through transactions or access fees.
Example: Open RAN platforms in telecom infrastructure
✅ Advantages: Scalability, Network effects
❌ Disadvantages: Requires critical mass, High development effort
➡️You can find more information on the topic of platform business models in the dedicated course.
💳 10. Leasing / Rental Model
Description: Temporary use of a product for a fee.
Example: Telecom hardware rented to businesses
✅ Advantages: Regular income, Lower entry barrier for customers
❌ Disadvantages: Maintenance costs, Leased hardware remains property of the provider
🧑🔧 11. Service and Maintenance Contracts
Description: Customers pay for regular support, updates, or maintenance.
Example: Maintenance contracts for data centers or router solutions with ISPs
✅ Advantages: Additional revenue post-sale, Long-term customer relationships
❌ Disadvantages: High personnel effort, Challenging SLA compliance
Downloads, Links and Templates
Understanding Business Models with over 100+ examples: https://businessmodelnavigator.com/
Busienss-Model-Navigator: Magic Triangle fra St. Gallen: https://dbd.au.dk/c/tools/magic-triangle
Business Model Canvas: https://seafile.rlp.net/d/c34afa92d64f46a6b830/
Lean Canvas Template by gründerplattform: https://tinyurl.com/leancanvasgruenderplattform
FAQ - Frequently asked questions
What exactly is the Business Model Navigator suitable for?
The Navigator uses over 50 proven models to show how successful companies design their business models. After the course, many people ask themselves, “Do I have to go through all of them?” No. It is enough to use a few suitable models as inspiration that fit your own project. The goal is not to copy, but to combine and adapt.
You can find an overview of over 100 business models at: https://businessmodelnavigator.com/.
Registration is required for an extended overview.
How do I choose the right business model patterns?
That depends on your industry, target group, and your problem. If you are still in the early stages, take three to five patterns that appeal to you spontaneously and see how you can translate them to your idea. You can refine your selection later.
What is the difference between a business model and a revenue model?
A business model describes how you create, distribute, and deliver value overall. The revenue model is only part of this and explains how you earn money. A good business model works even if the revenue model is tested and adjusted multiple times.
How do I test a revenue model without having the entire product ready?
A common thought is, “We can’t charge money before everything is working.” But that is exactly what is possible – for example, through landing pages with pricing options, pre-orders, small pilot projects, or conversations with potential customers. This allows you to find out early on whether customers are willing to pay.
What happens if customers don’t want to pay?
This is an important signal: either the benefit is not strong enough, or the revenue model is not suitable. In this case, you should review the value proposition or try alternative revenue models before completely abandoning the idea.
How detailed does our Business Model Canvas need to be?
Many founders ask whether the canvas has to be filled out perfectly right away. No—it is a living document. Start with assumptions, add to them with every insight from customer interviews or tests, and continuously adjust the fields. The canvas will become more precise over time.
How often should we review our business model?
Especially in the early stages, it is worth checking regularly—about once a month—whether the assumptions are still valid. Changes in the market or feedback from customers may require quick adjustments.
Can we pursue several business models at the same time?
Theoretically, yes, but in practice this is risky because resources are limited. For startups, it is advisable to start with a clear core model. Once this is up and running, you can add additional models (e.g., new sources of revenue).
How does the Business Model Canvas relate to the Business Model Navigator?
The Navigator provides inspiration through existing patterns, while the Canvas provides the structure to map your own model. So you can use the Navigator to gather ideas and then systematically present and review them in the Canvas.
Glossary
Business Model Navigator (BMN)
Short definition: An approach for systematically developing new business models based on 55 established patterns.
Benefit: Helps question existing logics and discover new approaches.
Phases: Initiation (understand problem), Ideation (adapt patterns), Integration (embed in model), Implementation (practical execution).
Example: Transferring the freemium pattern from the software industry to research data platforms.
Innovative Revenue Models
Freemium
Short definition: Basic version is free, premium functions are paid.
Benefit: Low entry barrier, broad user growth.
Example: Dropbox free, extra storage for payment.
Indirect Revenues
Short definition: Revenues are generated not directly by end users but by third parties.
Benefit: Unlocks alternative financing sources.
Example: In-app advertising, data licensing.
Direct Customer Relationship
Short definition: Revenues come from direct sales or contracts with end customers.
Benefit: Direct control over pricing and customer access.
Example: SaaS license model sold directly to companies.
Self-Service
Short definition: Customers perform tasks independently via digital channels.
Benefit: Scalability, lower costs.
Example: Online banking instead of branch visits.
“How can we improve?”
Short definition: Reflection question for continuous improvement of business and revenue models.
Benefit: Promotes innovation and adaptability.
Example: Testing new pricing models to increase customer loyalty.
Business Model Canvas (BMC)
Business Model Canvas
Short definition: Visualization of a business model in 9 building blocks.
Benefit: Makes business logic transparent, fosters team discussion.
Example: Mapping a platform with customer segments, partners, and revenues.
Value Proposition
Short definition: The value promise for customers.
Benefit: Shows why the offer is chosen.
Example: “Secure data transfer for research groups.”
Customer Segments
Short definition: Distinct groups of people or organizations a company addresses.
Benefit: Enables tailored offerings.
Difference from customer groups: Segments = strategic main target groups; groups = smaller subdivisions within a segment.
- Customer Segment
= a clearly defined target group with similar needs, willingness to pay, or behaviors.
Example: Research institutes as a customer segment for a cloud data platform. - Customer Group (within a segment)
= subdivision of a segment into smaller, more specific groups.
Example: Within the research institute segment:
• University labs (often smaller budgets, focus on flexibility),
• Industrial R&D departments (larger budgets, focus on data security).
Rule of thumb:
• Segment = strategic main target group
• Group = finer subdivision with slightly different requirements
Customer Relationship
Short definition: Type and intensity of interaction between a company and its customers.
Benefit: Strengthens trust and loyalty.
Example: Self-service vs. personal support.
Channels
Short definition: Paths through which a company communicates, sells, and delivers products.
Benefit: Determines reach and customer experience.
Example: Online shop, partner sales.
Key Partners
Short definition: External organizations or individuals essential to the business model.
Benefit: Provide missing resources or activities.
Example: Suppliers, research collaborations.
Key Activities
Short definition: Core activities required for value creation.
Benefit: Focuses on what drives the business model.
Example: Software development, marketing.
Key Resources
Short definition: The most important assets a company needs (physical, intellectual, human, financial).
Benefit: Foundation for implementing the business model.
Example: Development team, patents.
Revenue Models
Short definition: Mechanisms through which a company generates income.
Benefit: Ensures financial viability.
Example: Subscription, pay-per-use, licensing.
Cost Structures
Short definition: The sum of all costs incurred in executing the business model.
Benefit: Basis for pricing and profitability analysis.
Example: Personnel costs, infrastructure, marketing.
Checklist: Stress-Test Your Business Model
1. Foundations & Strategic Alignment
-
-
Is there a clear vision? (Long-term goal, societal or technological impact?)
-
Is there a clear mission? (How is the vision implemented through daily action?)
-
Is the core business clearly defined? (What is the company’s main focus?)
-
What are the core competencies? (What do we do better than others?)
-
2. Value Proposition & Customer Benefit
-
-
What customer problem are we solving?
-
What basic, additional, or added value does our product or service provide?
-
Is the customer benefit clearly and simply stated?
-
Do we have a clear Unique Selling Proposition (USP)?
-
3. Market & Target Audience
-
-
Has the target market been analyzed using structured methods?
-
What market segments have been identified? (Who exactly? Where? How big?)
-
Are reliable, up-to-date data and trends used in the market analysis?
-
Was the market possibly divided into niches?
-
4. Revenue Model
-
-
How exactly will the company generate revenue?
-
Is the revenue model innovative or traditional? (e.g., subscription, freemium, platform model)
-
Are there multiple revenue streams? (e.g., hardware + services)
-
Is the customer’s willingness to pay validated?
-
5. Value Chain Architecture
-
-
What are the key activities needed to deliver the solution?
-
What resources are essential (team, tech, IP)?
-
Which partners are required to make the model work?
-
Is the inter-company value chain clearly outlined?
-
6. Make or Buy – In-House vs. Outsourcing
-
-
Which components or services are provided in-house?
-
Which elements are outsourced?
-
Is there a well-reasoned make-or-buy decision?
-
7. Business System Overview
-
-
Is the interaction between all elements (customers, resources, partners, channels, etc.) clearly described?
-
Is there a visual or systemic representation of the business model?
-
Was a tool like the Business Model Canvas or a custom structure used?
-

Hi, i'm Lukas
and I manage the e-learning program. Do you have any further questions? Feel free to contact me via email: theisen@gruendungsbuero.info

